Freshness Factor: 10 Illustrations on How Fresh Content Can Influence Rankings |
| Freshness Factor: 10 Illustrations on How Fresh Content Can Influence Rankings Posted: 12 Dec 2011 01:06 PM PST Posted by Cyrus Shepard In 2003, engineers at Google filed a patent that would rock the SEO world. Named Document Scoring Based on Document Content Update, the patent not only offered insight into the mind of the world’s largest search engine, but provided an accurate roadmap of the path Google would take for years to come. In his series on the 10 most important search patents of all time, Bill Slawski shows how this patent spawned many child patents. These are often near-duplicate patents with slightly modified passages – the latest discovered as recently as October 2011. Many of the algorithmic changes we see today are simply improvements of these original ideas conceived years ago by Google engineers. One of these recent updates was Google’s Freshness Update, which places greater emphasis on returning fresher web content for certain queries. Exactly how Google determines freshness was brilliantly explored by Justin Briggs in his analysis of original Google patents. Justin deserves a lot of credit for bringing this analysis to light and helping to inspire this post. Although the recent Freshness Update received a lot of attention, in truth Google has scored content based on freshness for years. How Google Scores Fresh ContentGoogle Fellow Amit Singhal explains that “Different searches have different freshness needs.” The implication is that Google measures all of your documents for freshness, then scores each page according to the type of search query. While some queries need fresh content, Google still uses old content for other queries (more on this later.) Singhal describes the types of keyword searches most likely to require fresh content:
Google’s patents offer incredible insight as to how web content can be evaluated using freshness signals, and rankings of that content adjusted accordingly. Understand that these are not hard and fast rules, but rather theories consistent with patent filings, experiences of other SEOs, and experiments performed over the years. Nothing substitutes for direct experience, so use your best judgement and feel free to perform your own experiments based on the information below. Images courtesy of my favorite graphic designer, Dawn Shepard. 1. Freshness by Inception DateA webpage is given a “freshness” score based on its inception date, which decays over time. This freshness score can boost a piece of content for certain search queries, but degrades as the content becomes older. The inception date is often when Google first becomes aware of the document, such as when Googlebot first indexes a document or discovers a link to it.
2. Document Changes (How Much) Influences FreshnessThe age of a webpage or domain isn’t the only freshness factor. Search engines can score regularly updated content for freshness differently from content that doesn’t change. In this case, the amount of change on your webpage plays a role. For example, the change of a single sentence won’t have as big of a freshness impact as a large change to the main body text.
3. The Rate of Document Change (How Often) Impacts FreshnessContent that changes more often is scored differently than content that only changes every few years. In this case, consider the homepage of the New York Times, which updates every day and has a high degree of change.
4. Freshness Influenced by New Page CreationInstead of revising individual pages, websites add completely new pages over time. This is the case with most blogs. Websites that add new pages at a higher rate may earn a higher freshness score than sites that add content less frequently. Some SEOs insist you should add 20-30% new pages to your site every year. This provides the opportunity to create fresh, relevant content, although you shouldn’t neglect your old content if it needs attention.
5. Changes to Important Content Matter MoreChanges made in “important” areas of a document will signal freshness differently than changes made in less important content. Less important content includes navigation, advertisements, and content well below the fold. Important content is generally in the main body text above the fold.
6. Rate of New Link Growth Signals FreshnessIf a webpage sees an increase in its link growth rate, this could indicate a signal of relevance to search engines. For example, if folks start linking to your personal website because you are about to get married, your site could be deemed more relevant and fresh (as far as this current event goes.) That said, an unusual increase in linking activity can also indicate spam or manipulative link building techniques. Be careful, as engines are likely to devalue such behavior.
7. Links from Fresh Sites Pass Fresh ValueLinks from sites that have a high freshness score themselves can raise the freshness score of the sites they link to. For example, if you obtain a link off an old, static site that hasn’t been updated in years, this doesn't pass the same level of freshness value as a link from a fresh page – for example, the homepage of Wired.com. Justin Briggs coined this FreshRank.
8. Changes in Anchor Text Signals may Devalue Links |
| Wake Up SEOs, the New Google is Here Posted: 12 Dec 2011 01:51 AM PST Posted by gfiorelli1 This post was originally in YOUmoz, and was promoted to the main blog because it provides great value and interest to our community. The author's views are entirely his or her own and may not reflect the views of SEOmoz, Inc. No, not just because it decided I was not going to be not provided with useful information about my sites. And neither because it is changing practically every tool I got used since my first days as an SEO (Google Analytics, Webmaster Tools, Gmail…). And, honestly, not only because it released a ravenous Panda. No, the real question that is causing my headaches is: What the hell does Google want to go with all these changes? Let me start quoting the definition of SEO Google gives in its Guidelines: Search engine optimization is about putting your site's best foot forward when it comes to visibility in search engines, but your ultimate consumers are your users, not search engines. Technical SEO still matters, a lot!If you want to put your site’s best foot forward and make it the most visible possible in search engines, then you have to be a master in technical SEO. We all know that if we do not pay attention to the navigation architecture of our site, if we don't care about the on-page optimization, if we mess up with the rel=”canonical” tag, the pagination and the faceted navigation of our web, and if we don’t pay attention to the internal content duplication, etc. etc., well, we are not going to go that far with Search. Is all this obvious? Yes, it is. But people in our circle tend to pay attention just to the last bright shining object and forget what one of the basic pillars of our discipline is: make a site optimized to be visible in the search engines. The next time you hear someone saying “Content is King” or “Social is the new link building”, snap her face and ask her when it was the last time she logged in Google Webmaster Tools. Go fix your site, make it indexable and solve all the technical problems it may have. Just after done that, you can start doing all the rest. User is kingTechnical SEO still matters, but that does not mean that it is synonym of SEO. So, if you hear someone affirming it, please snap her face too. User and useful have the same root: use. And a user finds useful a website when it offers an answer to her needs, and if its use is easy and fast.. From the point of view that Google has of User, that means that a site to rank:
The first point explains the emphasis Google gives to site speed, because it is really highly correlated to a better user experience. The second is related to the quality of the content of a site, and it is substantially what Panda is all about. Panda, if we want to reduce it at its minimal terms, is the attempt by Google of cleaning its SERPs of any content it does not consider useful for the end users. The third explains the Schema.org adoption and why Google (and the other Search Engines) are definitely moving to the Semantic Web: because it helps search engines organize the bazillion contents they index every second. And the most they understand really what is your content about, the better they will deliver it in the SERPs. |
| You are subscribed to email updates from SEOmoz Daily SEO Blog To stop receiving these emails, you may unsubscribe now. | Email delivery powered by Google |
| Google Inc., 20 West Kinzie, Chicago IL USA 60610 | |











.jpg)
 I must admit that lately Google is the cause of my headaches.
I must admit that lately Google is the cause of my headaches.
 The decline of Link graph
The decline of Link graph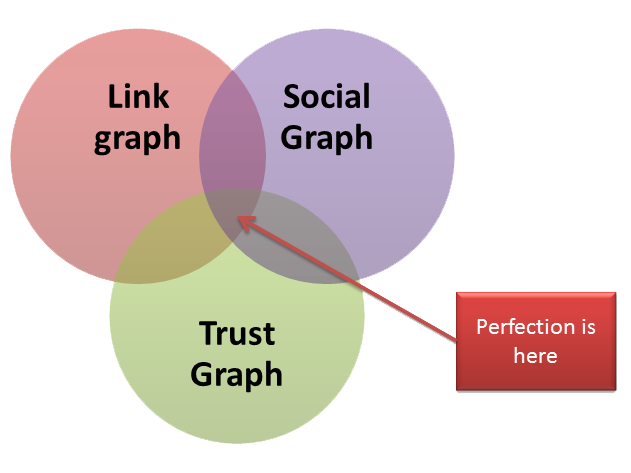



Niciun comentariu:
Trimiteți un comentariu